How We Built SAP-Level MDM on Frappe with MongoDB
Developed a scalableMDMsolution enabling seamless multi-sitedata synchronizationand eliminating dependency bottlenecks across distributed instances.
Problem Statement
Enterprise Challenge: Organizations using distributed instances across multiple business verticles faced critical data consistency issues, with master data scattered across instances creating synchronization nightmares, development bottlenecks, and operational inefficiencies that limited horizontal scalability and cross-site collaboration.
User Story
As a SAP expert at Reliance implementing Frappe Framework, it became increasingly difficult to maintain consistent master data across our distributed sites, leading to data silos, manual synchronization efforts, and deployment delays whenever master data changes were needed.
I wanted a centralized master data management system that could seamlessly share and synchronize data across all our Frappe instances in real-time, so that our teams could focus on business logic rather than data consistency issues, and we could scale horizontally without architectural constraints.
Existing Solution Analysis
Central Store-Based Sync (Kafka,RabbitMQ)
-
Used Oracle Golden Gate to publish events onto Kafka topics
-
Events are consumed by respective sites, maintaining their own copy
-
Limited central control over master version deprecation
Pull-Based Sync
-
Sites pulled the masters and maintained delta copies on the mutated masters
-
Attempted synchronization with parent schema
-
No communication mechanism for consumer registration tracking
Critical Gap: Both approaches lacked central control for deprecating and controlling master versions, with no visibility into consumer registration status or synchronization state.
Solution
Key Architecture
-
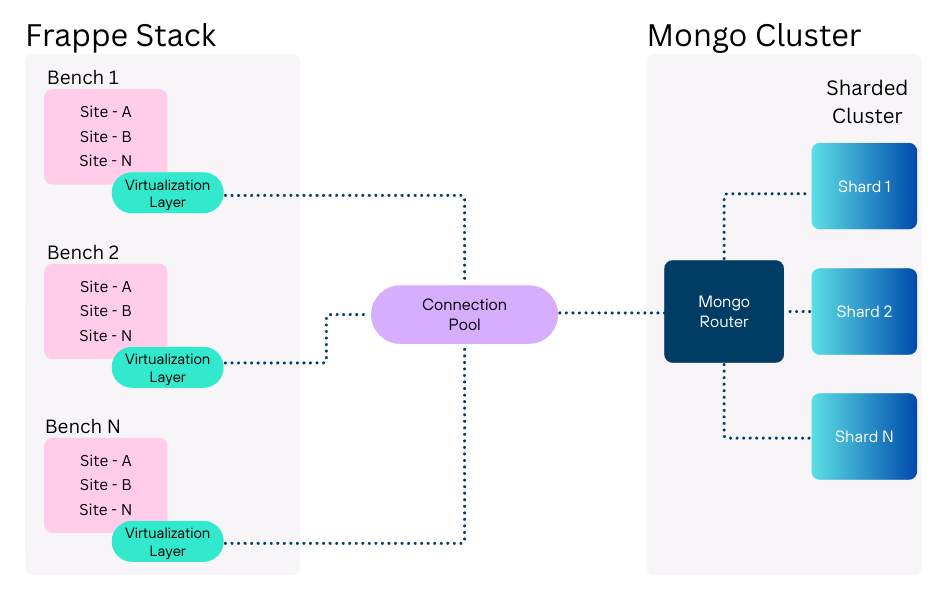
Virtual Doctype Extension: Built upon Frappe's virtual doctype architecture to create MDM-enabled document types
-
Centralized NoSQL Store: Implemented MongoDB as the master data repository with automated meta and data synchronization
-
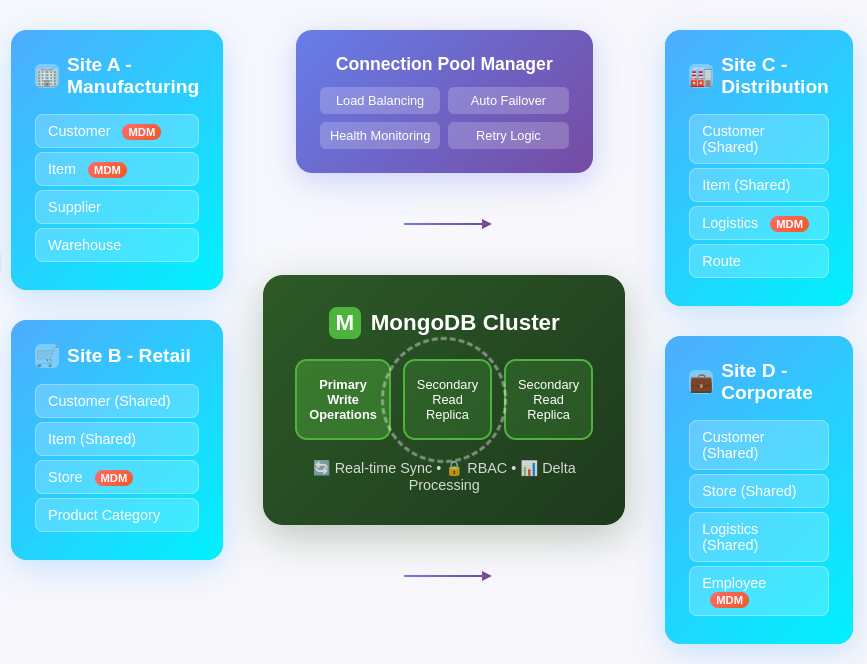
Connection Pool Management: Deployed connection pools to manage multi-instance and cluster connections to MongoDB efficiently
-
Read Replica Strategy: Utilized MongoDB read replicas to horizontally scale different shards of respective masters, requiring heavy read operations and deployment delays whenever master data changes were needed.
-
Cross-Site Communication: Developed secure sharing mechanisms with granular access control between Frappe instances
-
Real-time Verification: Created a validation system for data integrity across distributed environments
Frappe Virtualization Layer
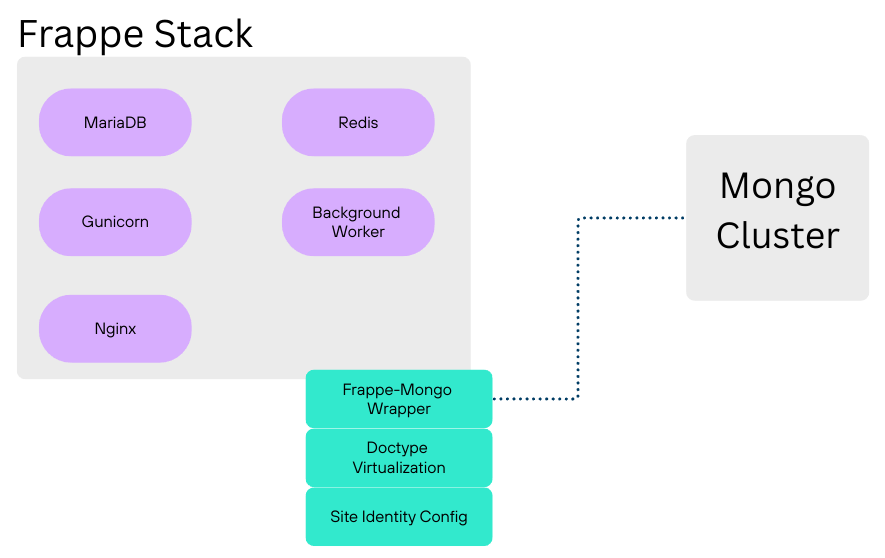
Frappe MongoDB Wrapper
A sophisticated database abstraction layer that seamlessly integrates MongoDB with Frappe's native ORM while preserving framework conventions:
-
Session Context Integration: Inherits and extends Frappe's database connection lifecycle, maintaining compatibility with existing session management, user contexts, and site-specific configurations
-
Connection Pool Optimization: Implements intelligent connection pooling with configurable timeouts, retry logic, and failover mechanisms for high-availability deployments
-
Query Translation: Automatically translates Frappe's SQL-like queries to MongoDB aggregation pipelines while maintaining semantic consistency
-
Transaction Simulation: Provides ACID-like behavior through MongoDB's multi-document transactions and custom rollback mechanisms
Doctype Virtualization Engine
An advanced doctype virtualization system that extends Frappe's virtual doctype capabilities for distributed master data management:
-
Dynamic Method Binding: Runtime interception and redirection of core doctype methods (save, delete, get_doc) to MongoDB operations while preserving Frappe's validation and hook system
-
Metadata Synchronization: Automated registration and synchronization of doctype schemas, custom fields, and business rules across MongoDB collections with versioning support
-
Permission Architecture: Granular role-based access control (RBAC) implementation that maps Frappe's permission system to MongoDB's field-level security model
-
Event System Integration: Seamless integration with Frappe's before/after hooks, validation events, and custom triggers for MongoDB operations
Site Identity Config
A centralized configuration and identity management system that handles multi-tenant MongoDB deployments:
-
Cluster Configuration: Manages MongoDB cluster topology, replica set configurations, and shard distribution strategies based on site-specific requirements
-
Identity Resolution: Provides secure site-to-site authentication and authorization mechanisms with encrypted token exchange and audit logging
-
Bootstrap Orchestration: Handles initial MongoDB collection setup, index creation, and seed data population during site provisioning
-
Background Job Context: Maintains MongoDB connection contexts for Frappe's background job system, ensuring consistent data access across async operations
Key Features Delivered
-
Master Data Declaration: One-click conversion of any virtual doctype into MDM master with automatic MongoDB integration
-
Migrate any existing doctype to MDM master
-
Use MDM doctype as a local doctype (Link fields, controls, etc)
-
Share any MDM master with sites across your infrastructure
-
Manage ACL and have version control over masters
-
Allow consumers to have their own data on top of any masters
-
-
Connection Pool Optimization: Efficient multi-instance cluster management with automatic failover and load balancing
-
Read Replica Scaling: Horizontal scaling through MongoDB read replicas for high-read master data scenarios
-
Granular Access Control: Site-specific sharing permissions through Frappe Shared Resource management interface
-
Delta Aggregation: Real-time delta processing using MongoDB aggregation framework for site-specific modifications
-
Consumer State Tracking: Automatic last sync, version, and registration status management for simplified ACL
-
Seamless Data Consumption: Simple consumption workflow allowing sites to access shared doctypes as local resources
-
Zero-Downtime Updates: Schema-less updates eliminate migration requirements and system downtime
Results & Achievements
Performance Improvements
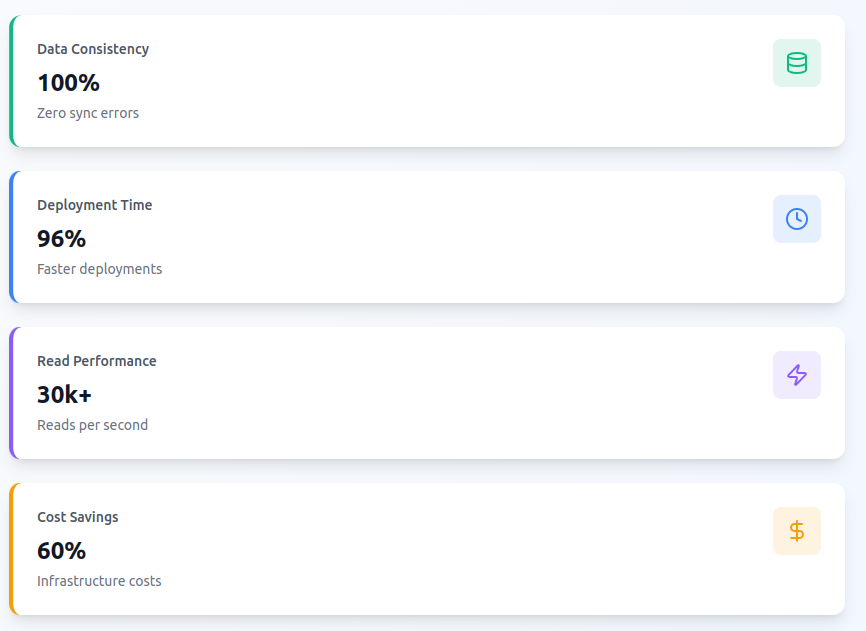
Business Impact
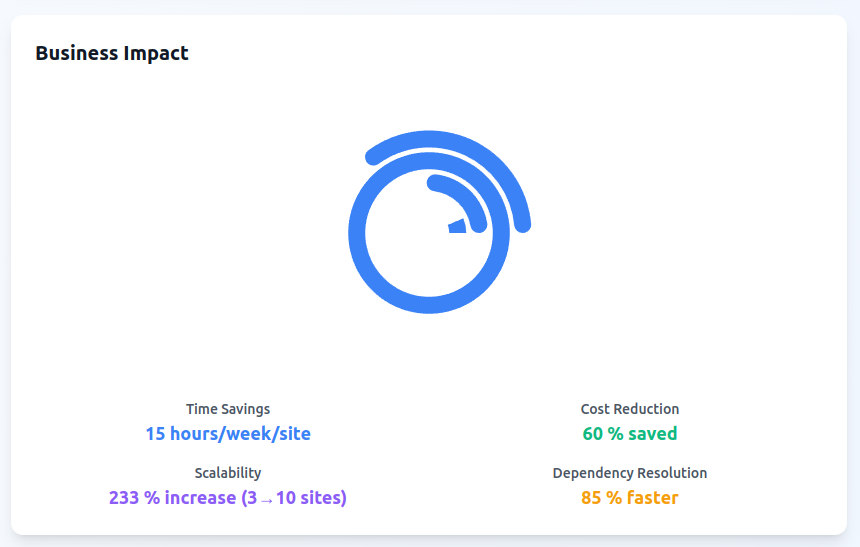

Conclusion
The Frappe MDM solution successfully addresses the critical challenge of master data management in distributed Frappe environments, providing enterprises with the scalability and consistency required for modern business operations. This framework establishes a foundation for future enhancements in cross-site collaboration and data governance.
Have a similar problem? We can consult scalix.in
Tags: #MDM #FrappeFramework #MongoDB #NoSQL #ConnectionPooling #ReadReplicas #DistributedSystems #DataManagement #SAP #Reliance #EnterpriseArchitecture #Scalability #CrossSiteSynct
© Copyright 2026. All Rights Reserved.